 |
EqWorld The World of Mathematical Equations |
 |
Exact Solutions > Integral Equations > Volterra Integral Equations of the First Kind and Related Linear Integral Equations with Variable Limit of Integration
1. Volterra Integral Equations of the First Kind
1-1. Integral equations with kernels involving power-law functions
-
 (x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).
(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 (Ax + Bt + C) y(t) dt = f(x).
(Ax + Bt + C) y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 (x − t)n y(t) dt = f(x),
n = 1, 2, ...
(x − t)n y(t) dt = f(x),
n = 1, 2, ...
-
 (x − t)1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
(x − t)1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 (x − t)−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
Abel equation.
(x − t)−1/2 y(t) dt = f(x).
Abel equation.
-
 (x − t)λ y(t) dt = f(x),
0 < λ < 1.
(x − t)λ y(t) dt = f(x),
0 < λ < 1.
-
 (x − t)−λ y(t) dt = f(x),
0 < λ < 1.
Generalized Abel equation.
(x − t)−λ y(t) dt = f(x),
0 < λ < 1.
Generalized Abel equation.
1-2. Integral equations with kernels involving exponential functions
-
 eλ(x−t) y(t) dt = f(x).
eλ(x−t) y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 eλx+βt y(t) dt = f(x).
eλx+βt y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 [eλ(x−t) − 1] y(t) dt = f(x).
[eλ(x−t) − 1] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 [eλ(x−t) + b] y(t) dt = f(x).
[eλ(x−t) + b] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 [eλ(x−t) −
eμ(x−t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
[eλ(x−t) −
eμ(x−t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 (eλx − eλt)−1/2
y(t) dt = f(x).
(eλx − eλt)−1/2
y(t) dt = f(x).
1-3. Integral equations with kernels involving hyperbolic functions
-
 cosh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
cosh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 {cosh[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cosh[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 {cosh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cosh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 cosh2[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
cosh2[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 sinh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
sinh[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 {sinh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
{sinh[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 sinh[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
sinh[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
1-4. Integral equations with kernels involving logarithmic functions
1-5. Integral equations with kernels involving trigonometric functions
-
 cos[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
cos[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 {cos[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cos[λ(x − t)] − 1} y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 {cos[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
{cos[λ(x − t)] + b} y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 sin[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
sin[λ(x − t)] y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 sin[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
sin[λ(x − t)1/2] y(t) dt = f(x).
1-6. Integral equations with kernels involving special functions
-
 J0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x).
J0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 J0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x).
J0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 I0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x).
I0(λ(x − t)) y(t) dt = f(x).
-
 I0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x).
I0(λ(x − t)1/2) y(t) dt = f(x).
10-7. Integral equations with kernels involving arbitrary functions
The EqWorld website presents extensive information on solutions to various classes of ordinary differential equations, partial differential equations, integral equations, functional equations, and other mathematical equations.
Copyright © 2004-2017 Andrei D. Polyanin
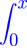 ln(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).
ln(x − t) y(t) dt = f(x).